THIS IS MY HOMEWORK PAGE I'LL DO MY HOMEWORK REGULARLY
Thursday, 30 June 2016
MOTION - Vaishnavi
MOTION
What is a motion?
The change of the postion of an object in terms of distance moved or te displacement
It could be uniform or non uniform depending on whether its velocity is constant or changing
Uniform motion : obeject covers equal distance onequal intervals of time
Non uniform motion:object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time
SCALER QUANTITY : The physical quantity in which only magnitude and direction is not specified .
ex: speed , distance
Examples
1) The object travels 16m in 4s and then another 16m in 2s what is the average speed?
Distance (s) =16m+16m=32m
Time taken (t) =4s+2s=6s
average speed(v) = Distance / Time
ie.v=s/t
=32m/6s=5.33m/s
2) The odometer of a car reads 2000km at the start of a trip and 2400km at the end of the trip. If the trip took 8h ,calculate the average speed of the car in km/h and m/s
Distance covered
s=2400km -2000km=400km
Time elapsed ,t =8h
average speed is:
vas =s/t =400km/8h
=50km/h
=50 km/h ×1000m/1km×1h/3600
=13.9m/s
3)Usha swims in 90m long pool.she covers 180m in one min by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight path. Find the average speed and average velocity of usha
Total distance in 1m is 180 m
Displacement of usha in 1 min = 0m
average speed =Total distance covered /Total time taken
=180 m/1min×180m/1min ×1min/ 60s
=3m/s
average velocity=displacement /time =0m/60s=0m/s
EXERCISE
1)An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200m in 40s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2min 20s?
Diameter of the circle =200m
Radius=100m
EXERCISE
1)An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200m in 40s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2min 20s?
Diameter of the circle =200m
Radius=100m
IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCES by Vaishnavi
CHAPTER-2
IS MATTER AROUND US PURE
Exercise
Q1- 1. Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
(a) Sodium chloride from its solution in water.
Evaporation
(b) Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride.
Sublimation
(c) Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car.
Filtration or Centrifugation or decantation
(d) Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
Chromatography
(e) Butter from curd.
Centrifugation
(f) Oil from water.
Using separating funnel
(g) Tea leaves from tea.
Filtration
(h) Iron pins from sand.
Magnetic separation
(i) Wheat grains from husk.
Winnowing
(j) Fine mud particles suspended in water.
Centrifugation
Q2- Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words: solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Answer
First, water is taken as a solvent in a saucer pan. This water (solvent) is allowed to boil. During heating, milk and tea leaves are added to the solvent as solutes. They form a solution. Then, the solution is poured through a strainer. The insoluble part of the solution remains on the strainer asresidue. Sugar added to the filtrate, which dissolves in the filtrate. The resulting solution is the required tea.
Q3- . Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below( results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
(a) What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 50 grams of water at 313 K?
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. What salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
Answer
(a) Since 62 g of potassium nitrate is dissolved in 100g of water to prepare a saturated solution at 313 K, 31 g of potassium nitrate should be dissolved in 50 g of water to prepare a saturated solution at 313 K.
(b) The amount of potassium chloride that should be dissolved in water to make a saturated solution increases with temperature. Thus, as the solution cools some of the potassium chloride will precipitate out of the solution.
(c) The solubility of the salts at 293 K are:
Potassium nitrate – 32 g
Sodium chloride – 36 g
Potassium chloride – 35 g
Ammonium chloride – 37 g
Potassium nitrate – 32 g
Sodium chloride – 36 g
Potassium chloride – 35 g
Ammonium chloride – 37 g
Ammonium chloride has the highest solubility at 293 K.
(d) The solubility of a salt increases with temperature.
Q4- . Explain the following giving examples:
(a) Saturated solution
(b) Pure substance
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension
Answer
(a) Solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at a particular temperature is known as saturated solution. For example in aqueous solution of sugar no more sugar can be dissolved at room temperature.
(b) A pure substance is a substance consisting of a single type of particles i.e., all constituent particles of the substance have the same chemical properties. For example water, sugar, salt etc.
(c) A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture whose particles are not as small as solution but they are so small that cannot be seen by naked eye. When a beam of light is passed through a colloid then the path of the light becomes visible. For example milk, smoke etc.
(d) A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solids are dispersed in liquids. The solute particles in suspension do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the medium. For example Paints, Muddy water chalk water mixtures etc.
Q5- . Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture.
Soda water, wood, air, soil, vinegar, filtered tea
Answer
Homogeneous mixtures: Soda water, air, vinegar, filtered tea
Heterogeneous mixtures: Wood, soil
Note: Pure air is homogeneous mixture but Polluted air is heterogeneous mixture.
Q6- . How would you confirm that a colourless liquid given to you is pure water?
Answer
Take a sample of colourless liquid and put on stove if it starts boiling exactly at 100 ºC then it is pure water. Any other colourless liquid such as vinegar always have different boiling point. Also observe carefully that after some time whole liquid will convert into vapour without leaving any residue.
Q7- . Which of the following materials fall in the category of a "pure substance"?
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric Acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air
Answer
The following materials fall in the category of a "pure substance":
(a) Ice
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
Q8- . Identify the solutions among the following mixtures:
(a) Soil
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water
Answer
The following mixtures are solutions:
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(e) Soda water
Q9- . Which of the following will show the "Tyndall effect"?
(a) Salt solution
(b) Milk
(c) Copper sulphate solution
(d) Starch solution
Answer
Tyndall effect is shown by colloidal solution. Here milk and starch solution are colloids therefore milk and starch solution will show Tyndall effect.
Q10-. Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures:
(a) Sodium
(b) Soil
(c) Sugar solution
(d) Silver
(e) Calcium carbonate
(f) Tin
(g) Silicon
(h) Coal
(i) Air
(j) Soap
(k) Methane
(l) Carbon dioxide
(m) Blood
Answer
Elements: Sodium, Silver, Tin and Silicon.
Compounds: Calcium carbonate, Methane and carbon dioxide.
Mixtures: Soil, Sugar, Coal, Air, Soap and Blood.
Q11- . Which of the following are chemical changes?
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Mixing of iron fillings and sand
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(f) Freezing of water
(g) Burning of candle
Answer
The following changes are chemical changes:
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
The following changes are chemical changes:
(a) Growth of a plant
(b) Rusting of iron
(d) Cooking of food
(e) Digestion of food
(g) Burning of candle
MOTION - Vaishnavi
MOTION
What is a motion?
The change of the postion of an object in terms of distance moved or te displacement
It could be uniform or non uniform depending on whether its velocity is constant or changing
Uniform motion : obeject covers equal distance onequal intervals of time
Non uniform motion:object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time
SCALER QUANTITY : The physical quantity in which only magnitude and direction is not specified .
ex: speed , distance
Examples
1) The object travels 16m in 4s and then another 16m in 2s what is the average speed?
Distance (s) =16m+16m=32m
Time taken (t) =4s+2s=6s
average speed(v) = Distance / Time
ie.v=s/t
=32m/6s=5.33m/s
2) The odometer of a car reads 2000km at the start of a trip and 2400km at the end of the trip. If the trip took 8h ,calculate the average speed of the car in km/h and m/s
Distance covered
s=2400km -2000km=400km
Time elapsed ,t =8h
average speed is:
vas =s/t =400km/8h
=50km/h
=50 km/h ×1000m/1km×1h/3600
=13.9m/s
3)Usha swims in 90m long pool.she covers 180m in one min by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight path. Find the average speed and average velocity of usha
Total distance in 1m is 180 m
Displacement of usha in 1 min = 0m
average speed =Total distance covered /Total time taken
=180 m/1min×180m/1min ×1min/ 60s
=3m/s
average velocity=displacement /time =0m/60s=0m/s
EXERCISE
1)An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200m in 40s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2min 20s?
Diameter of the circle =200m
Radius=100m
EXERCISE
1)An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200m in 40s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2min 20s?
Diameter of the circle =200m
Radius=100m
mumtaz jarra (10)
MOTION
EXAMPLES
1.an object travels 16 m in 4 sce then
another 16 m in 2 sec. what is the average speed of the object ?
answer. total distance travelled =16 +16 =32 m
total time taken =4 s + 2 s = 6 s
average speed = total distance travelled
------------------------
total time taken
= 32 m
----
6s
= 5.33 m/s
example 2
question : the odometer of a car reads 2000 km at the start of a trip. and 2400 km at the end of the trip.if the trip took 8 h caculate the average speed ofvthe car in km/h nd m/ s
answer: distance covered = 2400 km - 2000 km = 400 km
time elapsed t = 8 hour
average speed = s 400 km
- = ------
t 8 h
= 50 km 1000 1h
-- * ---- * ---
h 1km 36
= 13.9 m/s
example 3.
question; usha swims in a 90 m long pool. she coverrs 180 m in one minute by swimming feomcend end to the othwe end to and bacj aling the same srraight path.find tge average velocity of usha.
anawer. displacment of usha in 1 min = 0 m
average speed =total distance covered / totalvtym taken
= 180 m = 180 m / 1min * 1 min / 60 sec
= 3 m/s
average velocity = displacment / total time taken
= 0 m / 60 s
= 0 m/s
question : define the scaler quantty and name the 5 physical quantytity which are scaker
answer : the physical quantities in which oonly magnitude is measured and direction is not mention
examples : speed , distance
question : an athelete completes one round of a circilar track of diameter 200 m in 40 aec.what will be the distance covered and the displacmebt atvthe end of 2 minutes 20 sec.
answer : diameter of circular path = 200 m
radius of circular path = 200 / 2 = 100 m
time taken by athelete = 40 sec
distance covered ( s ) = 2 * 22/7
= 2 *22 / 7 * 100
speed = (v) = distance / time
= 2 * 2200 / 7 * 40
= 4400/ 7 * 40
distance covered in 140 s = speed * tine
4400 / 7*40*
no of round in 40 sec = 1
no of round in 140 sec = 140'/ 40 = 3 1/2
dispalacment =200 mi
questipn : a motorboat strom rest on a lake accelatres in a straight line at a cobstabt rate of 3.0 m/aec for 8.0 swc .how far does the boatvtravel during this time
EXAMPLES
1.an object travels 16 m in 4 sce then
another 16 m in 2 sec. what is the average speed of the object ?
answer. total distance travelled =16 +16 =32 m
total time taken =4 s + 2 s = 6 s
average speed = total distance travelled
------------------------
total time taken
= 32 m
----
6s
= 5.33 m/s
example 2
question : the odometer of a car reads 2000 km at the start of a trip. and 2400 km at the end of the trip.if the trip took 8 h caculate the average speed ofvthe car in km/h nd m/ s
answer: distance covered = 2400 km - 2000 km = 400 km
time elapsed t = 8 hour
average speed = s 400 km
- = ------
t 8 h
= 50 km 1000 1h
-- * ---- * ---
h 1km 36
= 13.9 m/s
example 3.
question; usha swims in a 90 m long pool. she coverrs 180 m in one minute by swimming feomcend end to the othwe end to and bacj aling the same srraight path.find tge average velocity of usha.
anawer. displacment of usha in 1 min = 0 m
average speed =total distance covered / totalvtym taken
= 180 m = 180 m / 1min * 1 min / 60 sec
= 3 m/s
average velocity = displacment / total time taken
= 0 m / 60 s
= 0 m/s
question : define the scaler quantty and name the 5 physical quantytity which are scaker
answer : the physical quantities in which oonly magnitude is measured and direction is not mention
examples : speed , distance
question : an athelete completes one round of a circilar track of diameter 200 m in 40 aec.what will be the distance covered and the displacmebt atvthe end of 2 minutes 20 sec.
answer : diameter of circular path = 200 m
radius of circular path = 200 / 2 = 100 m
time taken by athelete = 40 sec
distance covered ( s ) = 2 * 22/7
= 2 *22 / 7 * 100
speed = (v) = distance / time
= 2 * 2200 / 7 * 40
= 4400/ 7 * 40
distance covered in 140 s = speed * tine
4400 / 7*40*
no of round in 40 sec = 1
no of round in 140 sec = 140'/ 40 = 3 1/2
dispalacment =200 mi
questipn : a motorboat strom rest on a lake accelatres in a straight line at a cobstabt rate of 3.0 m/aec for 8.0 swc .how far does the boatvtravel during this time
keshav singh roll no. 31
MOTION
Question 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
Answer : Yes, an object even after it has moved through a distance, it can have zero displacement. As we know distance is just length of the path an object has covered irrespective of its direction or position with reference to certain point, where as the shortest distance measured from the initial to the final position of an object is known as the displacement.
For example, an object starts from point A and after covering a distance of say 50 meters, reaches at point B. Here after, it again moves back to point A.
Here the distance covered by object is = AB + BA = 50 m + 50 m = 100 m
where as displacement of object is = AB - BA = 50 m - 50 m = 0 m
As initial position of object is same as that of its final position hence its displacement, which is distance measured from the initial to the final position, is zero.
Question 2. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds from his initial position?
Answer : Suppose, a farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s as shown in the figure given below.
Which means the farmer will be at point C just diagonally opposite of point A
∴ Relative Displacement of farmer from point A at the end of 3 1/2 round will be = length of AC
which can be determined by the mathematical theorem as given below :
Question 3. Which of the following is true for displacement?
(a) It cannot be zero.
(b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Answer : Both of the statements are not true as
(a) Displacement can be zero
(b) Its magnitude is either less or equal to the distance travelled by the object
------------------------------------------------------
Page 102 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Answer : The speed of an object is the distance covered per unit time,and velocity is the displacement per unit time. The speed is a scalar quantity as it has just magnitude where as velocity is a vector quantity as it has both direction as well as magnitude.The speed can be changed by the distance travelled by a body in a particular time where as the velocity can be changed by changing the object's speed, direction of motion or both.
Question 2. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
Answer : The magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed, only when it is moving in a straight line.
Question 3. What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
Answer : Odometer of an automobile measures the distance covered by an automobile. All Automobiles are fitted with Odometer. Earlier Odometer used to be mechanical device, now a days we have electronic odometer.
Question 4. What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
Answer : The path of an object looks like a straight line when it is in uniform motion.j
Question 5. During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes.
What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is, 3 × 108 m s-1
Answer :
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 103 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration? (ii) nonuniform acceleration?
Answer : (i) A body is said to be in uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and
its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time
(ii) A body is said to be in nonuniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity is not constant .
Question 2. A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h-1 to 60 km h-1 in 5 s.
Find the acceleration of the bus.
Answer :
Question 3. A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed 40 km h-1 in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration.
Answer :
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 107 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
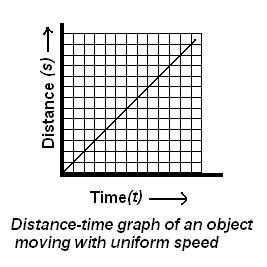
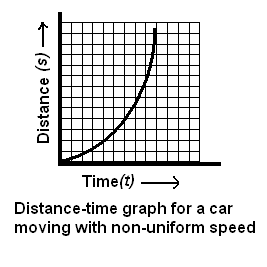
Question 1. What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Answer :
(i) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a straight line and not inclined along the time axis, as shown in the figure below
(iI) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a curve and as shown in the figure below
Question 2. What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer : Motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis is not moving at all and is in state of rest as shown in the figure below :
Question 3. What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer :The motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis indicates that the object is moving with uniform speed.
Question 4. What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
Answer :The area occupied below the velocity-time graph measures the distance covered by the object.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Question 1. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m s-2for 2 minutes.
Find (a) the speed acquired, (b) the distance travelled.
Answer :
Question 2. A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km h1 Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of -0.5 m s-2 Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Answer :
Question 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
Answer : Yes, an object even after it has moved through a distance, it can have zero displacement. As we know distance is just length of the path an object has covered irrespective of its direction or position with reference to certain point, where as the shortest distance measured from the initial to the final position of an object is known as the displacement.
For example, an object starts from point A and after covering a distance of say 50 meters, reaches at point B. Here after, it again moves back to point A.
Here the distance covered by object is = AB + BA = 50 m + 50 m = 100 m
where as displacement of object is = AB - BA = 50 m - 50 m = 0 m
As initial position of object is same as that of its final position hence its displacement, which is distance measured from the initial to the final position, is zero.
| A | >-----------50 m-------------> <-----------50 m-------------< | B |
Question 2. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds from his initial position?
Answer : Suppose, a farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s as shown in the figure given below.
Distance cover by the farmer as he moves from A to B to C to D to A, along the boundary wall of square field | = Perimeter of Square field | |
| = 4 x side of square field | ||
| = 4 × 10 m | ||
| = 40 m | ||
| ∴ speed of farmer | = 40 m/40 s | |
| = 1 m/s | ||
Distance covered by farmer in 2 minutes 20 seconds | = Speed × Time | |
| = 1 m/s × [(2×60) s + 20 s] | ||
| = 140 m | ||
Number of round in covering 40 m of distance along the boundary wall | = 1 round | |
∴ Number of round in covering 140 m of distance along the boundary wall | = 1×140 /40 rounds | |
| = 3.5 round | ||
| = 3 1/2 rounds |
∴ Relative Displacement of farmer from point A at the end of 3 1/2 round will be = length of AC
which can be determined by the mathematical theorem as given below :
| AC | = √AB2 + √BC2 |
| = √102 + √102 | |
| =10 √22 | |
| = 10 × 1.414 m | |
| = 14.14m |
Question 3. Which of the following is true for displacement?
(a) It cannot be zero.
(b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Answer : Both of the statements are not true as
(a) Displacement can be zero
(b) Its magnitude is either less or equal to the distance travelled by the object
------------------------------------------------------
Page 102 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Answer : The speed of an object is the distance covered per unit time,and velocity is the displacement per unit time. The speed is a scalar quantity as it has just magnitude where as velocity is a vector quantity as it has both direction as well as magnitude.The speed can be changed by the distance travelled by a body in a particular time where as the velocity can be changed by changing the object's speed, direction of motion or both.
Question 2. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
Answer : The magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed, only when it is moving in a straight line.
Question 3. What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
Answer : Odometer of an automobile measures the distance covered by an automobile. All Automobiles are fitted with Odometer. Earlier Odometer used to be mechanical device, now a days we have electronic odometer.
Question 4. What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
Answer : The path of an object looks like a straight line when it is in uniform motion.j
Question 5. During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes.
What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is, 3 × 108 m s-1
Answer :
| Speed of Signal (v) | = Speed of light |
| =3 × 108 ms-1 | |
| Time taken by Signal to reach the ground station (t) | = 5 minutes |
| = 5 × 60 seconds | |
| = 300 seconds | |
| Distance between the spaceship and the ground station (S) | = vt |
| = 3 × 108 m s-1 × 300 m | |
| =9×1010 m |
Page 103 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration? (ii) nonuniform acceleration?
Answer : (i) A body is said to be in uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and
its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time
(ii) A body is said to be in nonuniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity is not constant .
Question 2. A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h-1 to 60 km h-1 in 5 s.
Find the acceleration of the bus.
Answer :
| Initial Speed of the Bus (u) | = 80 km h-1 |
| = (80 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 800/36 ms -1 | |
| Final Speed of the Bus (v) | = 60 km h-1 |
| = (60 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 600/36 ms -1 | |
| Time in transition (t) | = 5 s |
| The acceleration of the Bus (a) | = (v-u) / t = [(800/36) - (600/36)] / 5 ms -2 = (-200/36) / 5 ms -2 = 5.55 / 5 ms -2 = 1.11 ms -2 |
Answer :
| Initial Speed of the Train (u) | = 0 ms -1 |
| Final Speed of the Train (v) | = 40 km h-1 |
| = (40 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 400/36 ms -1 | |
| Time in transition (t) | = 10 minutes |
| = 10 × 60 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| The acceleration of the Train (a) | = (v-u) / t = [(400/36) - 0] / 600 ms -2 = (11.11) / 600 ms -2 = 0.0185 ms -2 |
Page 107 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Answer :
(i) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a straight line and not inclined along the time axis, as shown in the figure below
(iI) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a curve and as shown in the figure below
Question 2. What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer : Motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis is not moving at all and is in state of rest as shown in the figure below :
Question 3. What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer :The motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis indicates that the object is moving with uniform speed.
Question 4. What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
Answer :The area occupied below the velocity-time graph measures the distance covered by the object.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 109-110 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m s-2for 2 minutes.
Find (a) the speed acquired, (b) the distance travelled.
Answer :
| Here as given, Initial speed (u) | = 0 | |
| Acceleration (a) | =0.1 m s-2 | |
| Time in transition (t) | =2 minutes | |
| =2 × 60 seconds= 120 s | ||
| We know that Final speed | = u + at | |
| ∴ (a) the speed acquired | = 0 + 0.1 m s-2 × 120 m s-1 | |
| = (1/10)120 ms-1 | ||
| = 12 ms-1 | ||
| = ut + (1/2)at2 | |
| ∴ (b) the distance travelled. | = 0 ×120 + (1/2) × 0.1×(120)2 | |
| = 0 + (120 × 120) /2 × 10 | ||
| = 14400/20 = 720 m | ||
| =720 m |
Question 2. A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km h1 Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of -0.5 m s-2 Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Answer :
| Given Initial speed of train (u) | =90 km h-1 |
| = (90 1000) / (60×60) m s-1 | |
| = 25 m s-1 | |
| Final speed of train (v) | = 0 ms1 |
| Braking acceleration (a) | = -0.5 m s-2 |
| We know 2as | = v2- u2 |
| Or distance (s) | =(v2-u2)/2a |
| ∴ Distance covered by the train before it came to rest | =(02-252)/(2 ×-0.5 )m |
| = - (25 × 25)×10/-1 m | |
| =625 m
FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE
CELL
Cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
Homework
Q. Why does the water come out from the cucumber when we add salt in it?
Ans- The salt cause water to be drawn out of the cucumber. Water is drawn to it because it goes from a higher concentration to the lower concentration. When there is random motion that will always happen and is called diffusion. In the cells of cucumber allows the water through but not the salt.
EXERCISE
Q.1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are also different from animal cells?
Ans - Plant Cell -1. Plant cells have cell wall.
2. Vacuole is large and present in centre of the cell.
3. They have plastids.
Animal cell- 1. Animal cells do not have cell wall.
2. Vacuole is small.
3. They do not contain plastids.
Q.2. How is prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Ans- Prokaryotic cell is generally smaller in size , nuclear region is poorly defined , the cell organelles are not membrane bounded and has a single chromosome.
Eukaryotic cell is generally larger in size , nuclear region is well defined with nuclear membrane. Membrane bounded cell organelles are present and has more then one chromosome.
Q.3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Ans- If plasma membrane ruptures or break down then the molecules of some substances will freely move in and out.
Q.4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no golgi apparatus?
Ans- Golgi apparatus has the function of storage , modification and packaging of the products in vesicles. If there were no golgi bodies , packaging and dispatching of materials synthesised by the cell will be stocked.
Q.5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? why?
Ans- Mitochondria is known as powerhouse of the cell because it releases the energy required for the different activities of life.
Q.6. Where do the lipids and the proteins consisting the cell membrane get synthesised ?
Ans- Lipids and proteins are synthesised in ER( Endoplasmic Reticulum).
Q.7. How does amoeba obtain it's food?
Ans- Amoeba take it's food by the cell membrane which forms the food vacuole.
Q.8. What is osmosis?
Ans- Osmosis is the process of movement of water molecule from a region of higher water concentration through a semi permeable membrane to a region of lower water concentration.
MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS
ACTIVITY- Q. Why do we observe that the level of water does not change even after dissolving salt in it?? ANS- When we dissolve salt in water , the particles of salt get into spaces between particles of water so this shows that the level of water does not change.
HOMEWORK
PROPERTIES OF PARTICLE
1. The particles of the matter are very small in size.
2. The particles of matter are continuously in motion , means they have kinetic energy.
3. The particles of matter have space between them.
Why solids are hard??
ANS- Solids are usually hard because they are tightly packed together and solids can maintain their shape own.
GIVE REASONS
Q.1. Why is table hard?
ANS- The table is hard because its rigidity is very high and
compressibility is not shown.
Q.2. Diver is able to cut water?
Ans- Water is fluid , i.e changes its shape when applied force.The diver is able to cut the water by applying force and changing its shape.
Q.3. The smell of hot sizzling food reaches our nose?
ANS- The smell of hot sizzling food reaches our nose as due to high speed of particles and large space between gases show the property of diffusing very fast into other gases.
Homework
Latent heat of fusion
The heat required to change 1 kg of solid into liquid completely is known as latent heat of fusion. It is absorbed by a body during a constant temperature process that is specified in some way.
Latent heat of vapourisation
The heat required to change 1 kg of liquid into vapours at atmospheric pressure is known as the latent heat of vapourisation.
Evaporation
The process of conversion of liquid into vapours is known as evaporation.
Factors affecting the rate of evaporation
1. Temperature- The rate of evaporation is directly proportional to the rise in temperature . more the temperature more will be the evaporation.
2. Humidity- The rate of evaporation is inversely proportional to the humidity. It means that the more the humidity is the less is the rate of evaporation.
3. Wind speed- The rate of evaporation is directly proportional to the wind speed. It means that more is the wind speed more will be the rate of evaporation.
4. Surface area- The rate of evaporation increases when the surface area increases as when the surface area will be increase the evaporation will also be increased.
EXERCISE
Q1. Convert the following into celsius scale-
(a) 293 K = 293-273 = 20*C
(b) 470 K = 470-273 = 197*C
Q2. Convert the following into kelvin-
(a) 25*C = 25 + 273 = 298 K
(b) 373*C = 373+273 = 646 K
Q3. Give reason for the following-
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Ans- It happen because naphthalene balls sublime and directly changes into vapour state without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away.
Ans- It happens because perfume contain volatile solvent and
diffuse faster and can reach people sitting several meters away.
Q4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles - water, sugar, oxygen.
Ans- Oxygen-water-sugar
Q5. What is physical state of water at-
(a) 25*C= liquid
(b) 0*C= solid or liquid
(c) 100*C= liquid and gas
Q6. Give reason-
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
Ans- Water at room temperature is a liquid because its freezing point is 0*C and boiling point is 100*C.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Ans- It is because the melting point of iron is higher than room temperature.
Q7. Why is ice a 273 K more effective in cooling than water a same temperature?
Ans-Ice at 273 K will absorb heat energy or latent heat from medium to overcome the fusion to become water. Cooling effect of ice is more than water at same temperature because water does not absorb extra heat from medium.
Q8. What produces more severe burns , boiling water or steam?
Ans- Steam at 100*C will produce more severe burns as extra heat is hidden in it called latent heat whereas the boiling water does not have this hidden heat.
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)