MOTION
Question 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example.
Answer : Yes, an object even after it has moved through a distance, it can have zero displacement. As we know distance is just length of the path an object has covered irrespective of its direction or position with reference to certain point, where as the shortest distance measured from the initial to the final position of an object is known as the displacement.
For example, an object starts from point A and after covering a distance of say 50 meters, reaches at point B. Here after, it again moves back to point A.
Here the distance covered by object is = AB + BA = 50 m + 50 m = 100 m
where as displacement of object is = AB - BA = 50 m - 50 m = 0 m
As initial position of object is same as that of its final position hence its displacement, which is distance measured from the initial to the final position, is zero.
| A | >-----------50 m-------------> <-----------50 m-------------< | B |
Question 2. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds from his initial position?
Answer : Suppose, a farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s as shown in the figure given below.
Distance cover by the farmer as he moves from A to B to C to D to A, along the boundary wall of square field | = Perimeter of Square field | |
| = 4 x side of square field | ||
| = 4 × 10 m | ||
| = 40 m | ||
| ∴ speed of farmer | = 40 m/40 s | |
| = 1 m/s | ||
Distance covered by farmer in 2 minutes 20 seconds | = Speed × Time | |
| = 1 m/s × [(2×60) s + 20 s] | ||
| = 140 m | ||
Number of round in covering 40 m of distance along the boundary wall | = 1 round | |
∴ Number of round in covering 140 m of distance along the boundary wall | = 1×140 /40 rounds | |
| = 3.5 round | ||
| = 3 1/2 rounds |
∴ Relative Displacement of farmer from point A at the end of 3 1/2 round will be = length of AC
which can be determined by the mathematical theorem as given below :
| AC | = √AB2 + √BC2 |
| = √102 + √102 | |
| =10 √22 | |
| = 10 × 1.414 m | |
| = 14.14m |
Question 3. Which of the following is true for displacement?
(a) It cannot be zero.
(b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Answer : Both of the statements are not true as
(a) Displacement can be zero
(b) Its magnitude is either less or equal to the distance travelled by the object
------------------------------------------------------
Page 102 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
Answer : The speed of an object is the distance covered per unit time,and velocity is the displacement per unit time. The speed is a scalar quantity as it has just magnitude where as velocity is a vector quantity as it has both direction as well as magnitude.The speed can be changed by the distance travelled by a body in a particular time where as the velocity can be changed by changing the object's speed, direction of motion or both.
Question 2. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
Answer : The magnitude of average velocity of an object is equal to its average speed, only when it is moving in a straight line.
Question 3. What does the odometer of an automobile measure?
Answer : Odometer of an automobile measures the distance covered by an automobile. All Automobiles are fitted with Odometer. Earlier Odometer used to be mechanical device, now a days we have electronic odometer.
Question 4. What does the path of an object look like when it is in uniform motion?
Answer : The path of an object looks like a straight line when it is in uniform motion.j
Question 5. During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five minutes.
What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal travels at the speed of light, that is, 3 × 108 m s-1
Answer :
| Speed of Signal (v) | = Speed of light |
| =3 × 108 ms-1 | |
| Time taken by Signal to reach the ground station (t) | = 5 minutes |
| = 5 × 60 seconds | |
| = 300 seconds | |
| Distance between the spaceship and the ground station (S) | = vt |
| = 3 × 108 m s-1 × 300 m | |
| =9×1010 m |
Page 103 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration? (ii) nonuniform acceleration?
Answer : (i) A body is said to be in uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and
its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time
(ii) A body is said to be in nonuniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity is not constant .
Question 2. A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h-1 to 60 km h-1 in 5 s.
Find the acceleration of the bus.
Answer :
| Initial Speed of the Bus (u) | = 80 km h-1 |
| = (80 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 800/36 ms -1 | |
| Final Speed of the Bus (v) | = 60 km h-1 |
| = (60 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 600/36 ms -1 | |
| Time in transition (t) | = 5 s |
| The acceleration of the Bus (a) | = (v-u) / t = [(800/36) - (600/36)] / 5 ms -2 = (-200/36) / 5 ms -2 = 5.55 / 5 ms -2 = 1.11 ms -2 |
Answer :
| Initial Speed of the Train (u) | = 0 ms -1 |
| Final Speed of the Train (v) | = 40 km h-1 |
| = (40 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) ms -1 | |
| = 400/36 ms -1 | |
| Time in transition (t) | = 10 minutes |
| = 10 × 60 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| = 600 s | |
| The acceleration of the Train (a) | = (v-u) / t = [(400/36) - 0] / 600 ms -2 = (11.11) / 600 ms -2 = 0.0185 ms -2 |
Page 107 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
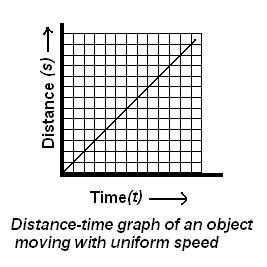
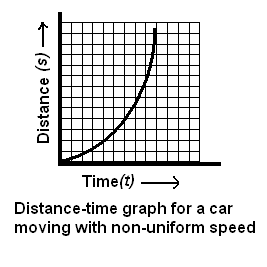
Question 1. What is the nature of the distance-time graphs for uniform and non-uniform motion of an object?
Answer :
(i) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a straight line and not inclined along the time axis, as shown in the figure below
(iI) For uniform speed, a graph of distance travelled against time is a curve and as shown in the figure below
Question 2. What can you say about the motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer : Motion of an object whose distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis is not moving at all and is in state of rest as shown in the figure below :
Question 3. What can you say about the motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis?
Answer :The motion of an object if its speed-time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis indicates that the object is moving with uniform speed.
Question 4. What is the quantity which is measured by the area occupied below the velocity-time graph?
Answer :The area occupied below the velocity-time graph measures the distance covered by the object.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 109-110 (CBSE Class IX ( 9th) Science Textbook - Chapter 8. Motion )
Question 1. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m s-2for 2 minutes.
Find (a) the speed acquired, (b) the distance travelled.
Answer :
| Here as given, Initial speed (u) | = 0 | |
| Acceleration (a) | =0.1 m s-2 | |
| Time in transition (t) | =2 minutes | |
| =2 × 60 seconds= 120 s | ||
| We know that Final speed | = u + at | |
| ∴ (a) the speed acquired | = 0 + 0.1 m s-2 × 120 m s-1 | |
| = (1/10)120 ms-1 | ||
| = 12 ms-1 | ||
| = ut + (1/2)at2 | |
| ∴ (b) the distance travelled. | = 0 ×120 + (1/2) × 0.1×(120)2 | |
| = 0 + (120 × 120) /2 × 10 | ||
| = 14400/20 = 720 m | ||
| =720 m |
Question 2. A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km h1 Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of -0.5 m s-2 Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Answer :
| Given Initial speed of train (u) | =90 km h-1 |
| = (90 1000) / (60×60) m s-1 | |
| = 25 m s-1 | |
| Final speed of train (v) | = 0 ms1 |
| Braking acceleration (a) | = -0.5 m s-2 |
| We know 2as | = v2- u2 |
| Or distance (s) | =(v2-u2)/2a |
| ∴ Distance covered by the train before it came to rest | =(02-252)/(2 ×-0.5 )m |
| = - (25 × 25)×10/-1 m | |
| =625 m |




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.